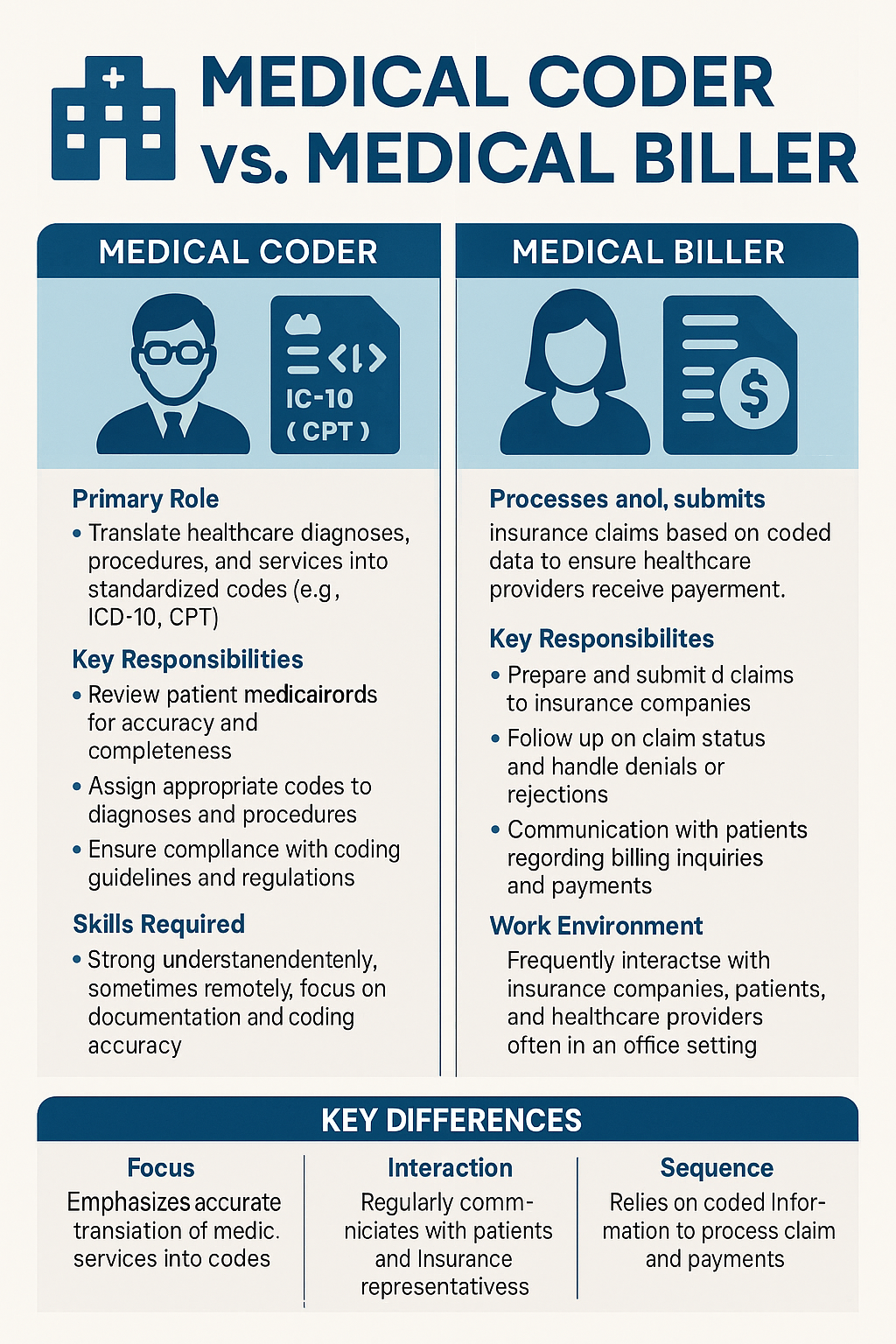
While medical coders and billers both contribute to the healthcare revenue cycle, their roles serve different but complementary purposes. Medical coders translate doctors’ notes, test results, and procedures into standardized codes like ICD-10 and CPT. These codes are essential for insurance documentation and accurate patient records. In contrast, medical billers take those codes and prepare claims, handle insurance submissions, follow up on payments, and manage patient billing inquiries. Coders focus on data accuracy; billers focus on financial flow.
Comparison Table: Medical Coder vs. Medical Biller
| Feature | Medical Coder | Medical Biller |
|---|---|---|
| Core Function | Translates healthcare data into codes | Manages insurance claims and payments |
| Tools Used | ICD-10, CPT, HCPCS, coding software | Billing software, payer portals, EHRs |
| Interaction with Patients | Rare to none | Frequent and ongoing |
| Typical Work Location | Remote, back office, hospital departments | Billing offices, front desk, remote |
| Primary Focus | Accurate clinical coding and compliance | Insurance reimbursement and billing cycles |
Best Certifications for Medical Coders vs Billers
Credentials play a key role in advancing your career in healthcare admin. They boost credibility, job opportunities, and salary potential.
Top Certifications for Medical Coders:
- CPC (Certified Professional Coder) – Widely respected credential from AAPC for outpatient settings.
- CCS (Certified Coding Specialist) – Offered by AHIMA, ideal for coders working in hospitals and facilities.
Top Certifications for Medical Billers:
- CPB (Certified Professional Biller) – AAPC certification focused on claims processing and billing workflows.
- CMRS (Certified Medical Reimbursement Specialist) – AMBA’s certification with a strong focus on reimbursement and compliance.
Professionals aiming for flexibility or working in smaller practices may choose to become both certified coders and billers.
Medical Coder vs Medical Biller Salary Comparison
Salaries vary by region, experience, certification, and type of employer.
- Medical Coders: Average salaries range from $47,000 to $60,000, with experienced or specialty coders earning even more.
- Medical Billers: Tend to earn between $40,000 and $55,000, with growth potential in management roles.
Holding certifications can lead to 20% higher pay compared to non-certified professionals.
Top Skills Needed for Medical Coding and Billing
To succeed in either field, you need a combination of technical know-how and soft skills.
Key Skills for Medical Coders:
- Deep understanding of medical terminology and anatomy
- Accuracy in applying codes based on documentation
- Familiarity with regulatory requirements like HIPAA and CMS guidelines
Essential Skills for Medical Billers:
- Knowledge of insurance claim cycles and denial management
- Strong interpersonal and problem-solving skills
- Ability to navigate payer portals and interpret EOBs (Explanation of Benefits)
Medical Coding vs Billing Job Outlook
The demand for both roles is growing steadily as healthcare expands.
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects an 8% growth in medical records and health information careers between 2022 and 2032. Telehealth, aging populations, and insurance complexities are fueling the need for skilled coders and billers.
Remote work is widely available, especially for coders, making it a flexible career choice.
Reviews of Medical Coding and Billing Programs
Choosing the right training program sets the foundation for success. Top-rated programs include:
- AAPC – Industry leader in certification and coding/billing education with career support
- AHIMA – Offers advanced coding and health information management training
- CareerStep – Self-paced, online programs with real-world coding and billing simulations
- Penn Foster – Affordable and structured, ideal for beginners with flexible scheduling
Make sure your chosen program is accredited and aligned with your career goals.
Medical Coder and Biller Job Satisfaction Rates
Both careers offer stability and satisfaction for people who enjoy organized, meaningful work.
Medical Coders report enjoying independent, detailed-oriented work, often with remote flexibility. Medical Billers often find fulfillment in helping patients understand their financial responsibilities and resolving claim issues.
Job satisfaction improves with ongoing training, supportive management, and access to modern tools.
Alternatives to Medical Coding and Billing Careers
Want something different but still within the healthcare space? Consider these alternatives:
- Health Information Technician – Manages and secures patient data in health records systems.
- Medical Administrative Assistant – Coordinates office tasks and schedules in clinics or hospitals.
- Patient Account Representative – Works closely with patients on billing questions and payment plans.
- Utilization Review Specialist – Evaluates healthcare services for medical necessity and cost efficiency.
Each role offers its own unique set of challenges and opportunities.
Medical Coding vs Billing: Which is Harder?
This depends on your strengths and preferences.
- Medical Coding can be complex due to the need to understand clinical language and coding rules. It’s best for those who enjoy deep focus and accuracy.
- Medical Billing demands patience, persistence, and people skills. If you’re organized and a good communicator, billing might be easier.
Both require lifelong learning due to frequent policy and technology updates.
Pros and Cons of Medical Coding and Billing
Benefits:
- Steady job growth in a recession-resistant industry
- Entry-level access with certification, no degree required
- Remote, freelance, and full-time work options
Challenges:
- Constantly changing guidelines from insurers and government
- Stress related to denied claims, deadlines, or difficult patient conversations
Understanding both sides helps you choose the career that aligns with your strengths.
Medical Coder vs Biller Work Environment Differences
These roles fit different personalities and work preferences.
- Medical Coders typically work behind the scenes, independently reviewing charts at a steady pace.
- Medical Billers work in faster-paced environments with lots of communication with patients, providers, and insurers.
Some organizations blend the roles, especially in smaller practices. Hybrid and remote setups are increasingly common.
Key Takeaways
- Coders focus on clinical documentation and standardized codes.
- Billers handle the financial side—submitting claims, following up, and collecting payments.
- Certifications are essential for credibility and higher income.
- Choose based on whether you prefer technical work (coding) or communication (billing).
FAQs
1. Can one person be both a medical coder and a biller? Yes. Especially in smaller clinics, it’s common for one person to handle both tasks. Dual training is a smart career move.
2. How long does training take for coding or billing? Most programs range from 6 to 12 months, depending on the course intensity and certification path.
3. Which role is better for remote work? Medical coding typically offers more remote flexibility due to the independent nature of the work.