Medical care becomes money through two connected jobs. Medical Coding turns diagnoses and procedures into ICD-10 Codes, CPT Codes and HCPCS Codes. Medical Billing uses those codes to submit claims, process payments, verify insurance and manage patient accounts so providers receive medical reimbursement.
How Medical Billing and Medical Coding differ in healthcare. We show roles like claim submission and insurance verification. We explain code sets like CPT, ICD-10, and HCPCS. Coders turn notes into codes. Billers submit claims and track payments.
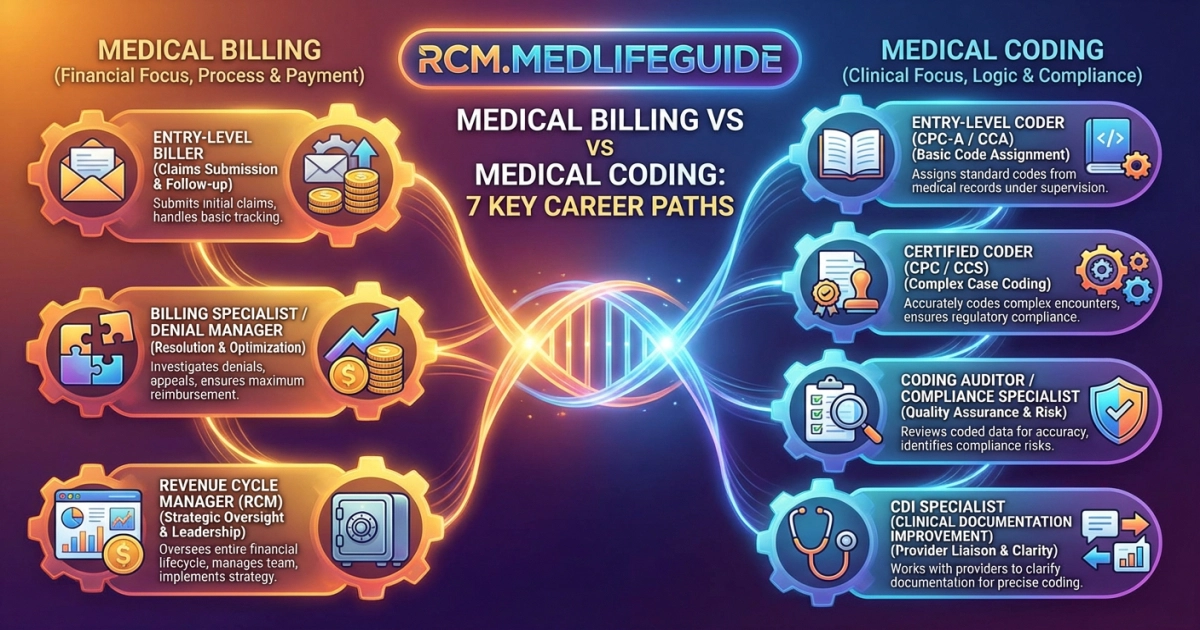
We cover seven career paths in Revenue Cycle Management. We explain training, software, denial management, compliance, and work settings. We guide you step by step so you can start with confidence.
Key Takeaways
- Medical coding translates clinical notes into ICD/CPT/HCPCS codes while medical billing turns those codes into insurance claims and patient invoices.
- Coding programs usually take 9–18 months and cost ~$2,000–$5,000 with certifications like CPC or CCA, while billing programs run 6–12 months at ~$1,200–$3,000 with CPB or CBCS options.
- Seven common career paths include medical coder, medical biller, combined billing/coding specialist, coding auditor, revenue cycle manager, compliance/HIM roles, and remote/freelance work.
- Coders generally earn slightly more because of technical expertise, both fields are growing, and cross-training increases job opportunities and earning potential.
- Strict compliance (HIPAA, False Claims) and emerging technologies (EHRs, AI automation, cloud billing) make certified, detail-oriented professionals necessary to reduce denials and optimize revenue.
Overview of Medical Billing and Coding Career Paths

| Career Path | Main Focus |
|---|---|
| Medical Coder | Assigns ICD-10 and CPT codes; follows Coding Guidelines and supports clinical documentation improvement |
| Medical Biller | Submits claims, posts payments and handles Denial Management and Claim appeals |
| Revenue Cycle Manager | Oversees Revenue Cycle Management, Billing Software and Healthcare Analytics and ensures compliance with HIPAA |
We use tools like Electronic Health Records, clearinghouses and practice management systems. Trends show rising automation and AI tools that can flag coding errors before Claim adjudication. This can improve cash flow but also raises the need for careful human review.
- Attention to detail: codes must match the patient record
- Compliance: follow HIPAA and coding compliance rules
- Career steps: certificate → CPC/CCA/CPB → RHIA or management roles
We compare costs and options like Home Chef, Factor 75 and Price per Meal when we talk about program value and how tuition stacks up against salary return.
Key takeaway: mastering both Medical Coding and Medical Billing or specializing in one gives a solid entry into Health Information Management and steady careers in healthcare administration.
Role of Medical Billers
We make sure doctors and clinics get paid by handling Medical Billing tasks. We check insurance, file claims and track payments in Patient Accounts and Billing Software.
We do Insurance Verification and prepare accurate Claim Submission. We use CPT Codes, ICD-10 Codes and HCPCS Codes. Then we follow up on Insurance claims and Claim adjudication to resolve denials and help clinics get paid faster.
- Verify coverage: confirm benefits and Payer policies
- Submit claims: use Claim scrubbing and RCM tools for clean claims
- Resolve denials: perform Denial Management and appeals
Coding accuracy and Coding compliance matter. A single wrong code can delay Medical Reimbursement or trigger Coding audits.
| Role | Main tasks | Tools / Codes |
|---|---|---|
| Medical Biller | Claims processing, EOB review and patient billing | Practice management software, RCM and EHR |
| Medical Coder | Assign codes, make sure Medical necessity and prepare charts | ICD-10, CPT codes and HCPCS codes |
We monitor Revenue Cycle Management (RCM). We use Healthcare Analytics and automation to reduce errors and speed Reimbursement. Future trends point to smarter Claim scrubbing that works closely with Electronic Health Records, making the whole process faster and more accurate.
Role of Medical Coders

Medical coders translate patient care into precise codes that help decide how hospitals and clinics get paid. Medical Coding uses ICD-10 Codes, CPT Codes and HCPCS Codes to record diagnoses, procedures and medical supplies.
We read clinical notes to assign codes and follow Coding Guidelines. We mark when Medical Necessity is met so claims move through Claims Processing and support correct Payer Reimbursement. Accurate coding reduces Claim Denial Management work and speeds Claim Submission, which helps clinics get paid faster and keeps patient billing clearer.
- Chart review: Read patient notes and encounter forms to find diagnoses and treatments
- Code selection: Use ICD-10, CPT and HCPCS to choose codes that match the documentation
- Audit and compliance: Perform coding audits and follow HIPAA and other Compliance Regulations
| Role | Key tools / impact |
|---|---|
| Medical Coder | ICD-10, CPT and HCPCS codes; EHRs and coding software; improves revenue cycle management |
| Medical Biller | Billing software, UB-04/Chargemaster and insurance verification; manages patient accounts and payments |
Good coding links clinical care to reimbursement. Weak coding creates denials, audits and lost revenue.
We combine knowledge of Electronic Health Records, Revenue Cycle Management and emerging Healthcare Analytics to improve accuracy. Automation and AI now assist coders but human review remains critical AAPC 2025.
Healthcare Administration Careers

We work with facts. Accurate Medical Coding and reliable Medical Billing keep clinics paid, protect patient records and power Revenue Cycle Management.
Medical Coding turns clinical notes into ICD-10 Codes, CPT Codes and HCPCS Codes. Coders follow Coding Guidelines and check Clinical documentation to make sure codes match what doctors record. Medical Billing handles claim submission, claims processing, insurance verification, patient accounts, denial management and medical reimbursement. Billing teams use Billing Software and Electronic Health Records to file claims and track payments.
- Medical coder: Translate visits into codes for claim submission
- Billing specialist: File claims, post payments, handle appeals and payer relations
- Revenue cycle manager: Oversee end to end revenue cycle management
- Health information manager: Maintain records and make sure HIPAA compliance
- Compliance officer: Audit coding compliance and regulations
- Billing software specialist: Configure EHRs and medical billing software
- Healthcare analyst: Use healthcare analytics to reduce denials and increase reimbursement
| Role | Focus |
|---|---|
| Medical Coder | Accuracy of ICD-10 and CPT Codes and documentation |
| Billing Specialist | Claims, payments, denial management and payer relations |
Careers in Healthcare Administration reward attention to detail, teamwork and tech skills. Courses in coding, billing and Electronic Health Records open doors.
We note trends. Automation and AI speed claim submission but require stronger coding compliance. Examples include Home Chef, Factor 75 and Price per Meal.
Revenue Cycle Management Positions

We run the teams that turn care into cash. Revenue Cycle Management connects clinical notes to payment. Medical Coding assigns ICD-10 Codes, CPT Codes and HCPCS Codes. Medical Billing uses those codes for Claim Submission, Claims Processing and Reimbursement. We check for Denial Management, Insurance Verification and Medical Necessity issues so providers get paid on time.
- Coding specialist: Assigns the correct codes to clinical notes and checks accuracy so claims are not denied.
- Billing specialist: Submits claims and follows up on payments and EOBs to keep revenue moving.
- Revenue cycle analyst: Uses healthcare analytics to find trends and fix problems that improve cash flow across the practice.
- Denial manager: Reviews denied claims, files appeals and works to reduce lost revenue.
- Patient accounts clerk: Manages patient balances and communicates clearly with patients about bills and payment options.
- Compliance officer: Enforces HIPAA rules and performs coding audits to keep records and billing correct.
- EHR and billing software lead: Integrates practice management systems and optimizes charge capture so services are billed accurately.
| Position | Primary focus |
|---|---|
| Coding Specialist | ICD-10 and CPT accuracy and correct use of coding guidelines |
| Billing Specialist | Claim submission and insurance verification to secure timely payment |
We balance patient care documentation, Electronic Health Records and billing software to protect revenue and meet Compliance Regulations.
Claims Processing Specialists

We make sure doctors and hospitals get paid. We guide the claims processing flow from the patient visit through medical reimbursement.
Core tasks we perform:
- Insurance verification: We check patient eligibility and payer policies so claims follow the rules.
- Accurate coding: We assign ICD-10 codes, CPT codes and HCPCS codes while following coding guidelines.
- Claim submission: We send claims using billing software and EHR or Electronic Health Records.
- Denial management: We appeal denials and track remittance advice to protect revenue.
- Step 1: Verify patient accounts and coverage.
- Step 2: Match documentation to codes for medical necessity.
- Step 3: Submit the claim and monitor the payer response.
| Role | Key impact |
|---|---|
| Claims Processing Specialist | Improves cash flow through accurate claim submission and denial reduction. |
| Medical Coder | Ensures compliance with coding, DRG and audit readiness. |
We use data and healthcare analytics to spot trends, cut denials and strengthen revenue cycle management.
Tip: We follow HIPAA and other compliance regulations. Tools like billing software and auditing help reduce errors. We even compare costs in unrelated areas for clarity, like Home Chef, Factor 75 and Price per Meal.
Insurance Verification Roles
Insurance verifiers confirm whether a patient’s plan will pay before care starts. We check benefits, co-pays and pre-authorization so claims move smoothly.
We work closely with Medical Billing and Medical Coding. Coders assign ICD-10 Codes, CPT Codes and HCPCS Codes, while verifiers update Patient Accounts and prepare accurate Claim Submission.
- Verify coverage: Contact insurance payers to confirm benefits and limits.
- Document findings: Enter results in
Electronic Health Records (EHR)and Billing Software. - Prevent denials: Flag medical necessity or coding issues to help with Denial Management.
| Role | Key focus |
|---|---|
| Insurance Verification | Benefits, pre-authorization and EOB checks |
| Medical Billing / Coding | Codes (ICD-10, CPT) Claim adjudication and Reimbursement |
Clear verification reduces denials and speeds medical reimbursement. That improves Revenue Cycle Management.
We follow Coding Guidelines, Compliance Regulations and HIPAA. We use Healthcare Analytics and Practice management software to track performance, a real-world mix of accuracy and communication that keeps clinics paid.
AAPC, AHIMA (industry standards) Explore careers in Health Information Management and Healthcare Administration.
Patient Accounts Management
We run patient accounts to make sure clinics get paid and patients understand bills. In Healthcare Administration we connect Medical Coding and Medical Billing to keep revenue moving. Coders assign ICD-10 Codes, CPT Codes and HCPCS Codes. Billers handle Claims Processing, Insurance Verification and Claim Submission.
Core duties:
- Patient accounts: We post payments, manage balances and explain charges.
- Claims processing: We prepare claims using coding guidelines and submit them to payers.
- Denial management: We track denied claims and file appeals to secure medical reimbursement.
| Task | Tools / Standards |
|---|---|
| Patient Accounts Management | Billing Software, Electronic Health Records and Insurance Verification |
| Claims & Coding | ICD-10 Codes, CPT Codes, HCPCS Codes and coding compliance |
| Examples / Notes | Home Chef, Factor 75 and Price per Meal |
We protect HIPAA compliance, perform coding audits and use Healthcare Analytics to improve revenue integrity. When documentation shows medical necessity, insurance reimbursement is faster. Tip: export EHR claims to a clearinghouse.
Accurate coding and clear patient accounts cut denials, speed payment and support stronger healthcare operations.
Health Information Management Careers
We separate the jobs so you can choose. Medical coding turns medical reports into ICD-10, CPT codes and HCPCS codes. Medical billing sends claims, checks insurance and posts payments using billing software and electronic health records.
- Medical coder: Translates patient charts into the right codes using coding guidelines so clinics receive accurate reimbursement.
- Medical biller: Files claims, follows up on claims processing and manages patient accounts until payments are posted.
- Health information manager: Oversees health information management and enforces compliance regulations to keep records correct and legal.
- Revenue cycle analyst: Optimizes revenue cycle management and claim scrubbing to reduce delays and improve cash flow.
- Coding auditor: Reviews work for coding compliance and helps improve clinical documentation so codes match the care provided.
- Denial management specialist: Handles claim denials, writes appeals and runs denial management processes to recover payments.
- Healthcare analytics specialist: Uses data from electronic health records to help with payer adjudication and forecasting.
| Focus | Top tools / skills |
|---|---|
| Coding accuracy | ICD-10, CPT, HCPCS and coding guidelines |
| Payment flow | Billing software, claims processing and prior authorization |
We advise you to learn both basics. Coding accuracy reduces denials and smart billing speeds reimbursement. Together they protect patient data and clinic revenue.
Healthcare Analytics Opportunities
We find strong opportunities where Healthcare Analytics meets Medical Billing and Medical Coding. By studying Electronic Health Records and insurance claims we uncover wasted costs. This work speeds Revenue Cycle Management and improves Medical Reimbursement.
We draw on data from ICD-10 Codes, CPT Codes and HCPCS Codes plus Claims Processing logs to predict Claim denials. The data guides Denial Management and tightens Compliance Regulations such as HIPAA compliance. Advanced models flag problems with Documentation integrity or missing Medical Necessity evidence before Claim Submission, so teams can fix issues early and avoid delays in payment.
- Analytics roles: Build dashboards that track Patient Accounts and payer trends
- Automation: Integrate Billing Software and EHRs to reduce manual Insurance verification
- Audit & quality: Use analytics for Coding audits and optimal Modifier usage
| Medical Billing | Medical Coding |
|---|---|
| Focus: Claim Submission, payments and appeals | Focus: Diagnosis codes, Procedure codes and accuracy |
| Tools: Medical billing software and remittance advice | Tools: Coding Guidelines and code sets (ICD-10 CPT) |
We recommend learning both coding and analytics. The combination multiplies value in Health Information Management and Revenue cycle management.
CPT: 99213 ICD-10: E11.9 These examples show how codes feed analytics. U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2024
Frequently Asked Questions
Typical education: certificate/diploma programs (billing ~6–12 months, $1,200–$3,000; coding ~9–18 months, $2,000–$5,000) plus industry certs (billers: CPB/CBCS; coders: CPC/CCA/CCS) with entry-level pay around $37–40K, average coders ~$45–48K and billers ~$40–45K, and certified/specialized or combined roles often $50K+ with better prospects as experience and credentials grow.
Seven key paths: Medical coder (translates charts into ICD/CPT/HCPCS codes; detail-focused), Medical biller (submits claims, manages payments/appeals; payer- and patient-facing), Billing & coding specialist (combined generalist for smaller practices), Coding auditor/compliance specialist (reviews accuracy, prevents fraud and denials), Clinical documentation improvement (CDI) specialist (partners with clinicians to improve records for accurate coding/reimbursement), Revenue cycle/billing manager (oversees operations, staff and cash flow), and Health information manager/director (manages medical records, policy, analytics and higher-level HIM strategy).
Medical coding translates clinical diagnoses, procedures and services into standardized ICD/CPT/HCPCS codes, while medical billing uses those codes to prepare and submit insurance claims, manage denials, post payments and handle patient billing to secure provider reimbursement.
Ending
We say Medical Coding turns medical notes into standard codes. We say Medical Billing sends claims and gets payments from insurers. We recommend choosing the path that fits our skills or training for both. Next step: tell us which call to action you want: course info, job help, or a study plan.
Most Searched Topic By Medical Biller and Coders You can find them on the home page of this website https://rcm.medlifeguide.com