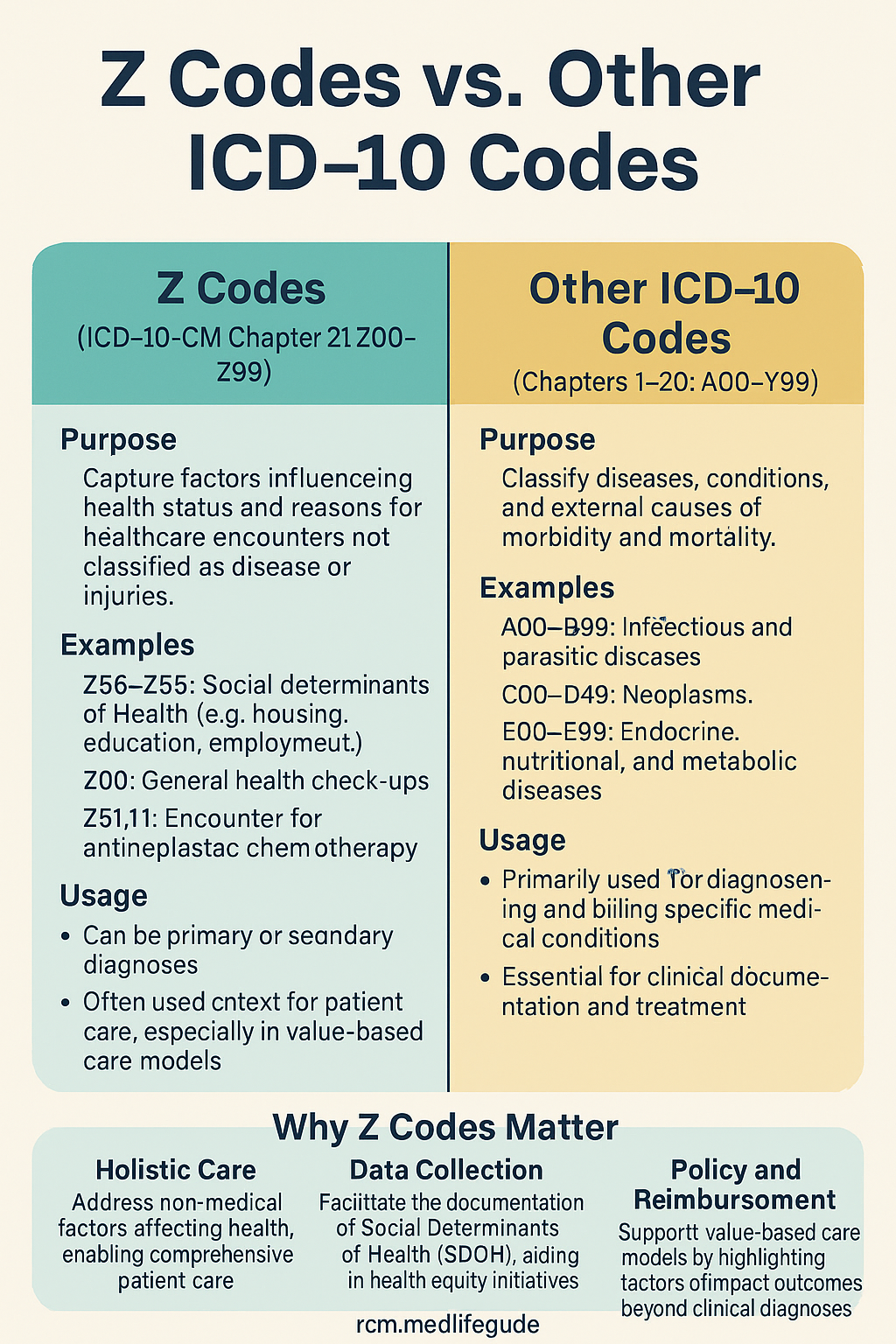
Z codes in the ICD-10-CM system stand out because they don’t represent diseases, but rather reasons for healthcare encounters that affect a patient’s overall health or well-being. While traditional ICD-10 codes reflect diagnoses, Z codes document social, behavioral, and environmental factors, which can be vital in holistic treatment planning and preventive care.
🧠 What Are Z Codes?
Z codes (found in the range Z00–Z99) are used to report:
- Factors influencing health status (like homelessness, unemployment)
- Preventive care visits (such as vaccinations or screenings)
- Administrative reasons (e.g., exams, follow-up care, aftercare)
Unlike other ICD-10 codes, Z codes are not always tied to a medical diagnosis.
🆚 Z Codes vs. Traditional ICD-10 Codes: Key Differences
| Feature | Z Codes | Other ICD-10 Codes |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Document reasons for healthcare encounters | Indicate specific diagnoses or conditions |
| Scope | Behavioral, social, lifestyle, preventive | Disease-focused |
| Mandatory or Optional Use? | Often optional but recommended | Typically required for billing |
| Claim Reimbursement | Limited, may not trigger payment alone | Often required for reimbursement |
| Examples | Z59.0 (Homelessness), Z23 (Immunization) | E11.9 (Diabetes), I10 (Hypertension) |
🎯 When to Use Z Codes
Use Z codes when:
- The patient is not sick but needs care (e.g., flu shot).
- There are non-medical issues impacting health (e.g., domestic violence, housing insecurity).
- Follow-ups, counseling, or screening tests are involved.
✅ Benefits of Using Z Codes
- Provides fuller picture of patient’s needs
- Improves care coordination
- Supports population health tracking
- Helps in addressing social determinants of health (SDOH)
📊 Infographic Snapshot: Understanding Z Codes
- 70% of healthcare outcomes are influenced by social and environmental factors
- Only ~2% of claims include Z codes—this gap highlights missed opportunities
- Top used Z codes: Z00.00 (General exam), Z23 (Immunization)
🧩 Bullet Points Summary
- Z codes = non-disease-related codes
- Highlight social needs, preventive care
- Improve patient-centered documentation
- Often underutilized in clinical coding
- Support value-based care models
A: Some Z codes support payment when paired with a primary diagnosis. Alone, many Z codes don’t trigger reimbursement but are vital for accurate records.
A: No. Z codes cover social situations, screenings, follow-ups, counseling, and even chronic condition influences.
A: They offer insight into patients’ social context, help improve care outcomes, and support quality measures in value-based care.